I love to read. To my mind, if you’re a business leader, you can’t afford not to. I often hear excuses. Some people are too busy – life is hectic and there’s no time. Others say reading isn’t for them or they simply don’t enjoy it. But it sharpens memory and brain function like nothing else, allowing you to think more critically. In the business world, if you aren’t able to use your intellectual abilities to make informed decisions, you’re unlikely to succeed.
Marcus Buckingham’s books are a great example. They’ve been hugely influential in my life. ‘First Break All The Rules’ introduced me to tools like the Gallup Q12 and StrengthsFinder, setting me off on a strengths-based path ever since. So, I was really intrigued to read his latest book, ‘9 Lies About Work’. In fact, it’s been so thought-provoking I’ve decided to devote an entire blog to it.
Buckingham wrote this book jointly with Ashley Goodall, Senior Vice President of Leadership and Team Intelligence at Cisco. As a result, it contains a great combination of Buckingham’s research and Goodall’s practical experience of the concepts. It’s deliberately confrontational, challenging some of the ‘well-known truths’ that are widely held in the corporate world. So, what are the nine lies about work – and do I agree?
Lie #1: People care which company they work for
This really resonated with me. The idea that once you’ve joined a company, you care much more about the team you’re in rather than the organisation. I’ve been saying for years that an employee’s experience of work will always be viewed through the lens of their team and manager. In this chapter, the authors present evidence that backs this up.
There’s no doubt that potential recruits care about the company initially. So your organisation needs a strong employer brand backed up by positive GlassDoor ratings and digital messaging. But once in, the way team leaders interact with new recruits is everything. Churn and productivity are not evenly spread – they tend to correlate with the effectiveness or otherwise of team leaders.
What’s interesting is that’s exactly what I discussed with Nic Marks, CEO of Friday Pulse, in our podcast interview recently. They found that teams with the highest levels of happiness in their Friday pulse survey were 22% more productive than those who had the least. In my own experience, wherever we’ve stripped out silos and put together small, cross-functional teams focused on a specific customer cohort, there was greater clarity and higher levels of engagement. This engagement is a function of that specific team’s dynamic. There is nothing that an executive team can do, no lever that it can pull, that isn’t related to team leaders.
Mechanisms for measuring engagement can be really helpful here and these are discussed in the book with a suggested re-working of the Gallup Q12. I would say it’s important to make sure that any metric gives you some indication of team leader performance. I’d suggest a lagging indicator that gives results based on staff churn and also productivity per team.
Lie #2: The best plan wins

Hmmm – this is true to a certain extent. However, I’ve always believed in establishing a regular rhythm to help with planning and achieving goals. Changing the cadence in an organisation can be hugely powerful.
Buckingham and Goodall are saying that instead of a 3 or 5-year plan, it’s better to have flexibility so that people aren’t demotivated or demoralised by not hitting goals. Yes – agility is important. The plan is less important than planning.
Lie #3: The best companies cascade goals
This really made me bristle. Here, the book takes a swipe at smart goals, KPIs and OKRs as a general thing. They say they’re a waste of time. As I read this, I felt they were talking about large corporates and not the smaller, growing businesses that I work with. I know that in large organisations, the bureaucratic machine can slow things down until goals become irrelevant. Certainly, if they work on an annual cycle, using tools like yearly appraisal systems, goals can be a complete waste of time. But the businesses I coach have the ability to move much faster, rolling out OKRs swiftly as part of a quarterly, agile cycle and ensuring everyone knows what’s required of them to meet their targets.
Where I do agree is the importance of cascading down purpose and making individuals accountable for their own decisions. Building plans from the bottom up has got to be a good thing. It’s true that staff are more likely to be motivated by a goal they set themselves rather than one that’s imposed on them. I’ve seen this with my own eyes. If you coach someone to come up with an objective, they typically come up with something that’s more of a stretch and are more motivated to achieve it because it’s theirs (you can apply the same theory to small children!)
Lie #4: The best people are well rounded

So interesting, this point. By coincidence, I’ve chatted to a number of clients recently about exactly this. There’s a common perception that to do well in life, you need to be good at everything. In the corporate world, this manifests in managers focusing on weaknesses, using them as a reason why someone isn’t promoted or given a pay rise.
It’s the opposite of a strengths-based approach. And I completely agree – it’s a lie. We all have innate strengths. In ‘9 Lies’, the authors talk about Lionel Messi, the best footballer in the world, who happens to be left-footed. It’s amazing that in his early life, his coaches didn’t force him to play more with his right foot. They allowed him to perfect his left foot. This starts early in life. As parents, we say we want well-rounded children. But do we really? If your child is good at the guitar, surely they should focus on that, not on learning a different instrument.
Successful people are often amazing at one thing – so amazing that they attract followers who forgive them any weaknesses because their main strength is so amazing. Don’t expect a goalkeeper to score goals. He’s 6 foot tall with really big hands! Encourage strengths and celebrate excellence and let’s forget about well rounded.
Lie #5: People need feedback

Really? Not sure about this one. In the book, the authors argue that feedback puts people’s brains into fight or flight mode which means they don’t absorb any learning from the experience. But how can we improve unless we know how we impact others? Everyone has a ‘back-hand’ – a part of themselves they can improve with focused effort. If tackled sensitively, I do think there’s a place for feedback.
It’s true that every person will come at feedback from a different perspective, based on their own unique experience. My strengths will always be different from yours so if I recommend corrective action, it will always be coming from my way of doing it. Our outcome may be the same, but the way we get there is likely to be completely different.
Far better to turn it around. Rather than telling people how they’re doing and suggesting corrective action, ask them how they feel. You’re more likely to get to the root of an issue if you understand it more deeply. You may get some insight into why your behaviour is having a certain impact on someone. This may not be your intention, but now that you know about it, you can do something about it. Or maybe you can agree and understand that you both approach the same thing in different ways.
By focusing on feelings, you’re discussing performance in a different way that translates easily into a team setting. For example, if someone isn’t pulling their weight, instead of pointing the finger at them and telling them to work harder, the rest of the team can express their feelings of frustration. Food for thought!
Lie #6: People can reliably rate other people
Buckingham and Goodall argue that, because all opinions are subjective, it’s impossible for one person to rate another at work. Yes – I get that. One person’s definition of what good looks like can be very different from another’s. This is why interviews are often inconsistent. There is always unconscious bias. The person being interviewed will have a completely different set of skills but will be measured against a subjective viewpoint.
Metrics like the Gallup Q12 can be really useful here. Instead of rating others, it places the emphasis on the individual. ‘Someone around here cares about me’. ‘In the last 7 days, I have received praise’ etc etc. By focusing on an individual’s personal experience, it becomes an objective measure of engagement.
So don’t ask people to rate each other ask them how they feel – they can understand the question and their answer is valid.
Lie #7: People have potential
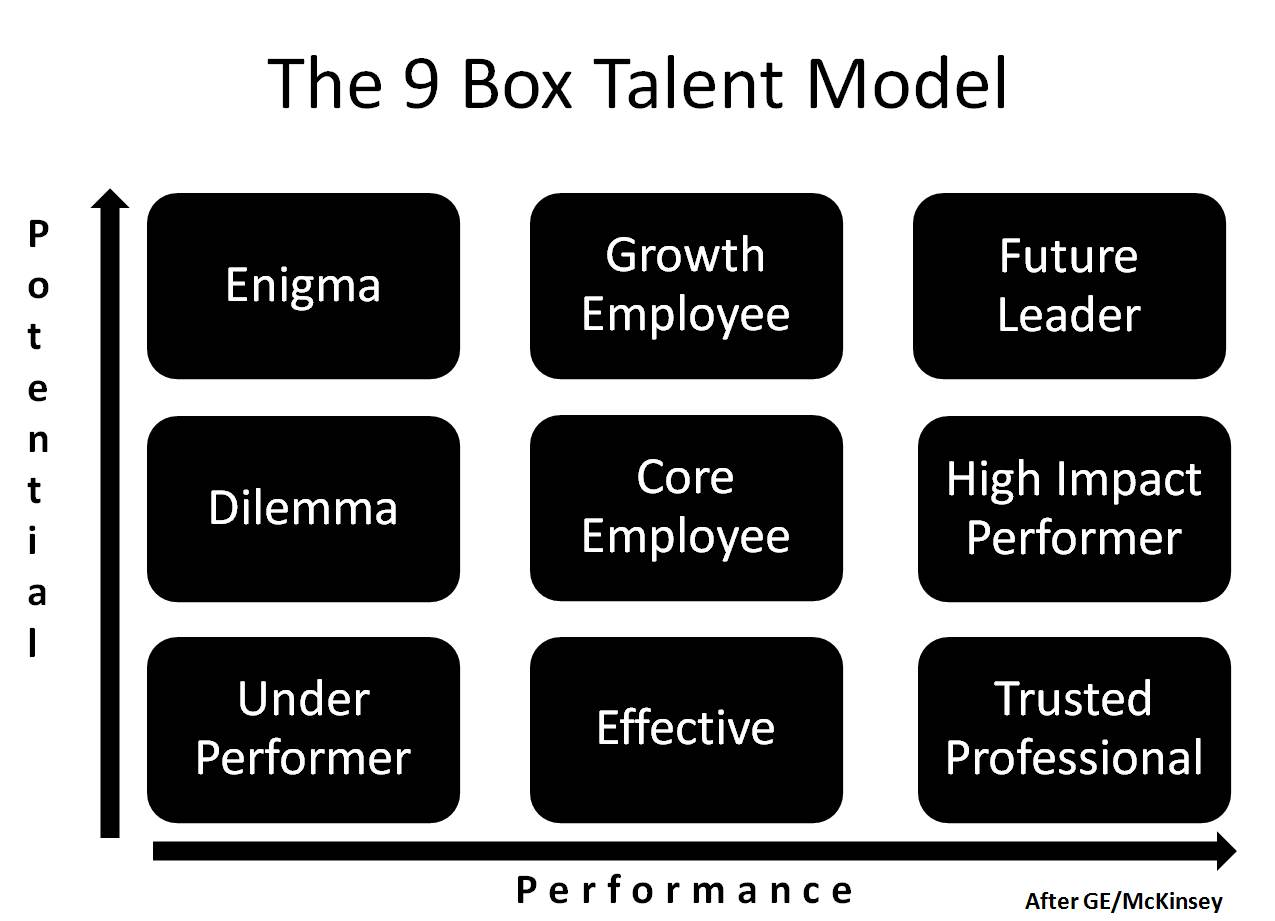
The 9 Box Grid is meaningless. Man, it was good to read that! Wherever I’ve come across this tool plotting employee performance against potential, I’ve thought the same thing. Buckingham and Goodall take a big swipe at it calling it totally ineffective – it’s your subjective measure of others.
Too right. It’s another one of those things that small companies think will make them look bigger. So, they introduce it when it’s totally unnecessary. People need to look for evidence. The 9 Box Grid is a non-research based, HR construct with very little value for employee development. Bin yours now.
Lie #8: Work-life balance matters most
Now, this is an interesting spin on what I’ve been saying for a while. If you talk about balancing work as a bad thing and life as good, you’re embarking on mission impossible. Far better to focus on doing more of what you love and less of what you loathe, both at work and at home.
I was reminded of this when chatting to a neighbour at a party recently. He’d just retired at 72 so we talked about why he’d carried on working beyond the point many of us call it a day. He said his company had reduced his hours to three days a week by taking out all the areas of his job that he hated. As a result, he’d been happy to carry on and really enjoyed the last few years of his career. He would have carried on if his wife hadn’t given him an ultimatum!
Employers need to prioritise joy in people’s working lives. Wherever I’ve been MD, we’ve put a cap on commuting distance. At Peer 1, we didn’t recruit anyone who had longer than a 45-minute commute. Evidence showed us that people stop being fully engaged at that point as the journey is so dismal.
It’s also why I hate job descriptions – this idea that the job is going to be done the same by everyone. At Rackspace, we took a much more fluid approach. If we were recruiting a new person for a team, we’d ask the existing members to tell us which parts of their job they hated. Then we’d recruit for someone who loved to do these things.
It was great to read some of the research in this chapter. Cisco had gone onto a more agile cycle and noticed that check-ins or one-to-ones with managers made a massive difference to productivity. They had rolled these out globally but inconsistently. As a result, they got an amazing set of data where they could track performance against the frequency of one-to-ones. If these took place weekly, there was a massive uptick in productivity. This dropped dramatically when one-to-ones were monthly and at six weeks or more, they had a negative impact, meaning you were better off not doing them at all. This adds weight to my theory that annual appraisals are a total waste of time. If you’re looking for something to make a difference in productivity, introduce a coaching intervention every week.
Lie #9: Leadership is a thing
The final conclusion that ‘Nine Lies’ builds towards is that you can’t teach leadership. Sending someone on a two-day, leadership course and expecting a radical transformation is ridiculous. Totally agreed. How many of us have experienced bad management? People who are promoted to leadership roles because they were the best salesperson or developer without any natural, innate qualities for leadership?
The authors say leaders are nothing without followers. If you inspire others with your particular strength, people will gravitate towards you. At all the companies I’ve run in the UK, we provided volunteer opportunities for staff to run charity committees or social projects where they could naturally demonstrate their leadership qualities. This was a great way to test them out – to see if they could inspire a team to follow them.
So overall, a fascinating and challenging book with some interesting takeaways. Definitely worth putting on your holiday reading list!
Written by business coach and leadership coaching expert Dominic Monkhouse. Contact him to schedule a call here. You can order your free copy of his book, Mind Your F**king Business here.

